Execution Model¶
To execute a primitive, a user needs to pass memory arguments and a stream to
the dnnl::primitive::execute() member function.
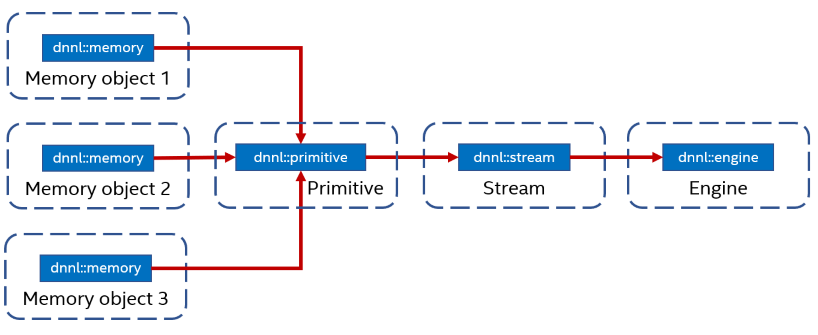
The primitive’s computations are executed on the computational device corresponding to the engine on which the primitive (and memory arguments) were created and happens within the context on the stream.
Engine¶
Engine is abstraction of a computational device: a CPU, a specific GPU card in the system, etc. Most primitives are created to execute computations on one specific engine. The only exceptions are reorder primitives that transfer data between two different engines.
Engines correspond to and can be constructed from pairs of the DPC++
sycl::device and sycl::context objects.
-
struct
dnnl::engine¶ An execution engine.
Public Types
Public Functions
-
engine()¶ Constructs an empty engine. An empty engine cannot be used in any operations.
-
engine(kind akind, size_t index)¶ Constructs an engine.
- Parameters
akind: The kind of engine to construct.index: The index of the engine. Must be less than the value returned by get_count() for this particular kind of engine.
-
engine(kind akind, const cl::sycl::device &dev, const cl::sycl::context &ctx)¶ Constructs an engine from SYCL device and context objects.
- Parameters
akind: The kind of engine to construct.dev: SYCL device.ctx: SYCL context.
-
cl::sycl::context
get_sycl_context() const¶ Returns the underlying SYCL context object.
-
cl::sycl::device
get_sycl_device() const¶ Returns the underlying SYCL device object.
-
Stream¶
A stream is an encapsulation of execution context tied to a particular
engine. They are passed to dnnl::primitive::execute() when executing a
primitive.
Stream attributes are used to extend stream behavior in an implementation-defined manner.
-
struct
dnnl::stream_attr¶ A container for stream attributes.
Streams correspond to and can be constructed from DPC++ sycl::queue
objects. Alternatively, oneDNN can create and own the corresponding objects
itself. Streams are considered to be ephemeral and can be created / destroyed
as long these operation do not violate DPC++ synchronization requirements.
Similar to DPC++ queues, streams can be in-order and out-of-order (see the
relevant portion of the DPC++ specification for the explanation). The desired
behavior can be specified using dnnl::stream::flags value. A stream
created from a DPC++ queue inherits its behavior.
-
struct
dnnl::stream¶ An execution stream.
Public Types
-
enum
flags¶ Stream flags. Can be combined using the bitwise OR operator.
Values:
-
enumerator
default_order¶ Default order execution. Either in-order or out-of-order depending on the engine runtime.
-
enumerator
in_order¶ In-order execution.
-
enumerator
out_of_order¶ Out-of-order execution.
-
enumerator
default_flags¶ Default stream configuration.
-
enumerator
Public Functions
-
stream()¶ Constructs an empty stream. An empty stream cannot be used in any operations.
-
stream(const engine &aengine, flags aflags = flags::default_flags, const stream_attr &attr = stream_attr())¶ Constructs a stream for the specified engine and with behavior controlled by the specified flags.
- Parameters
aengine: Engine to create the stream on.aflags: Flags controlling stream behavior.attr: Stream attributes.
-
stream(const engine &aengine, cl::sycl::queue &queue)¶ Constructs a stream for the specified engine and the SYCL queue.
- Parameters
aengine: Engine object to use for the stream.queue: SYCL queue to use for the stream.
-
cl::sycl::queue
get_sycl_queue() const¶ Returns the underlying SYCL queue object.
- Return
SYCL queue object.
-
enum